Algorithmic trading has become central to India’s equity and derivatives markets. What began as a niche, institution-driven workflow is now widely adopted across proprietary desks, quant funds, and sophisticated retail users. With increasing automation, SEBI and the stock exchanges have established a comprehensive regulatory framework to ensure market integrity, manage systemic risk, and promote fair access. For brokers, understanding this landscape is no longer optional—algo compliance is now a core supervisory function.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
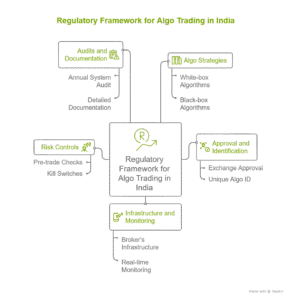
With algorithmic trading becoming increasingly popular among retail investors, SEBI has introduced a comprehensive framework to safeguard market integrity. The regulations focus on transparency, investor protection and accountability. Brokers and algo providers must meet these regulatory requirements before offering any algorithmic trading products to clients.
Mandatory exchange approval
Brokers must obtain exchange approval for every algo strategy before it goes live, ensuring that only tested and verified strategies operate in the market. SEBI keeps the definition of algorithmic trading intentionally broad—any computer-driven decision about price, quantity, timing or order modification is considered algo trading, even in simple automated tools.
Broad classification of Algo strategies
Algo strategies generally fall into two categories-
White-box algorithms are fully transparent, with clear and disclosed logic. For instance, a strategy that buys when the price crosses a moving average and sells when it falls below. Both brokers and exchanges can easily understand how these algorithms make decisions.
Black-box algorithms, on the other hand, use complex or proprietary logic- which is not disclosed. Because of this less visibility, SEBI requires providers offering black-box strategies to register as Research Analysts. This ensures they maintain proper documentation and research-style explanations of the strategy’s intent and methodology, even if the exact code remains confidential.
Approval, Identification and Version Control
Before an algorithm goes live, the broker must get it approved by the exchange. Every strategy—white-box or black-box—must be documented, tested and certified, and any change in logic requires fresh approval. Each approved algorithm receives a Unique Algo ID, which is attached to every order so regulators can easily trace its activity.
There are many algo trading platform solutions in the market, but they can’t just offer strategies freely. Their strategies must be backed by registered RAs and get their algorithms approved by the exchange before any broker can onboard them.
Algorithms hosted on Brokers infrastructure
SEBI has discontinued open APIs, which previously allowed traders and third-party apps to connect directly to a broker’s platform. Now, access will be permitted only through controlled setups that allow clear identification of algorithmic activity. All algorithms must run on the broker’s own infrastructure, with no execution on external servers, cloud systems or unmanaged third-party environments unless they are formally integrated into the broker’s framework.
Risk Controls and Operational Safeguards
The regulatory framework places strong emphasis on pre-trade risk checks. Every order must pass through validations for price limits, quantity limits, margins and order throttle limits (orders per second) before reaching the exchange.
Brokers must also implement safeguards such as kill switches, cancel-on-disconnect logic, exposure controls and mandatory 2FA authentication for user access.
Technology Infrastructure and Monitoring
Algo trading requires a tightly controlled technology environment. Brokers must ensure that production servers, access permissions and backup systems meet regulatory expectations. Continuous, real-time monitoring is essential, with brokers expected to track patterns, modifications, unusual behaviour and overall system performance. SEBI does not define specific latency levels, but it does expect consistency, fairness and complete logging of all decisions and order flow.
Audits and Documentation
Every broker offering algo trading undergoes an annual system audit by a SEBI-approved auditor. The audit reviews risk systems, approvals, version control, deployment practices, access rights and logs. Good documentation is essential; logs often become the primary source of truth for regulators.
Regulatory Direction
The industry expects clearer rules for marketplace-style algo platforms, better disclosures around backtesting, stronger supervision tools and more defined responsibilities for algo developers. As automation spreads further into retail participation, regulation will continue to evolve.
As algo trading becomes deeply embedded in India’s market structure, regulatory expectations continue to rise. When brokers work with algo trading solution providers that maintain rigorous approvals, testing and risk controls, it strengthens their own compliance posture and reduces operational strain, enabling them to grow in a safe and future-ready manner.














